Proteomics
See Figure 2 for the meanings of the abbreviations used in this chapter.
1. LC-MS (DDA) for proteomics
1-1 Input data
The dataset for reproducing this tutorial can be obtained from https://zenodo.org/records/15369007
This tutorial utilizes 2 raw data files (*.raw) from https://repository.jpostdb.org/entry/JPST000200.
The human_proteins_ref.fasta was obtained from https://www.uniprot.org/.
1-2 Starting up your project

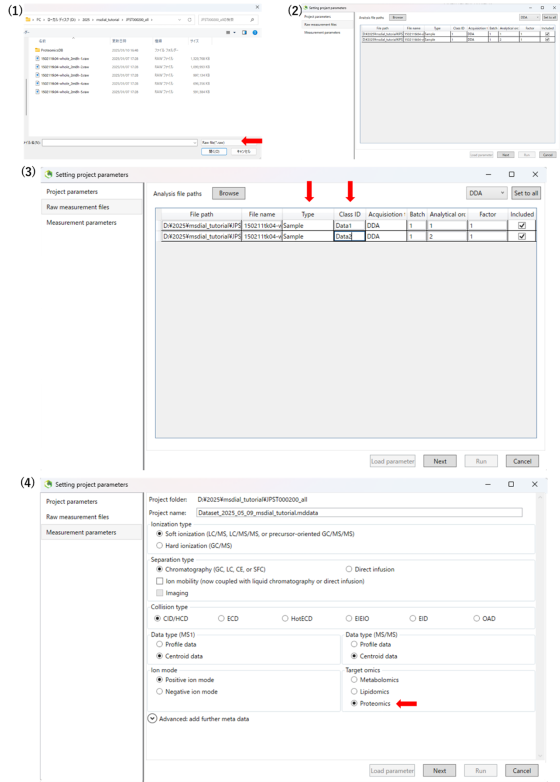
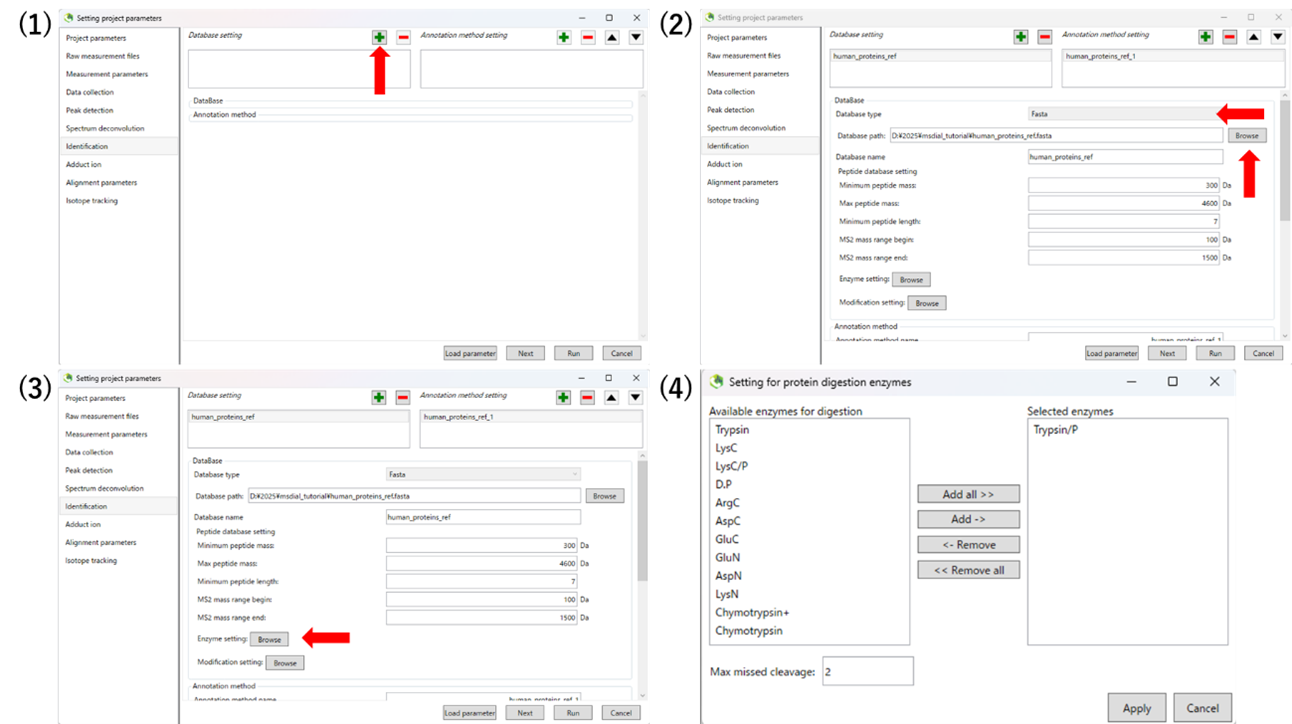
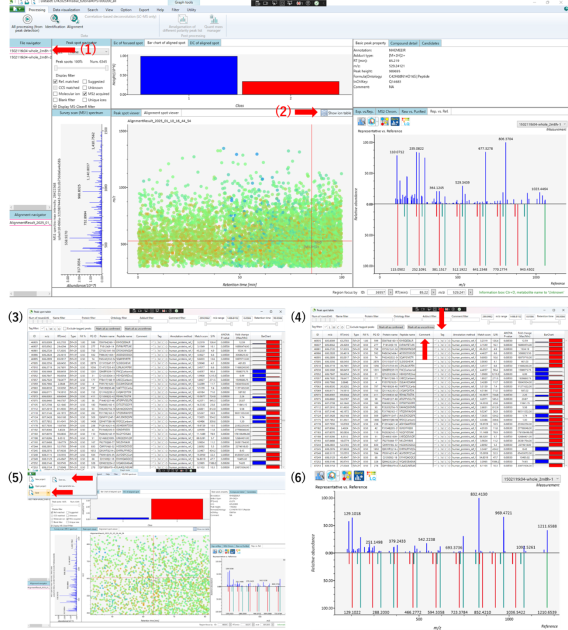
The video tutorial for the MS-DAIL5 operation