Duplicate alignment spot feature to separate isomers
Importance of MS-Dial in duplicating the alignment spot feature to separate isomers
MS-DIAL is a powerful, open-source software platform designed for the comprehensive analysis of untargeted metabolomics and lipidomics data. In some cases, lipids and metabolites are quantified in their isomeric forms by MS-DIAL, making it essential to accurately identify and quantify these isomers. Proper identification and quantification are critical for understanding the diverse biological functions of these compounds, as isomers can have distinct roles in biological processes.
Purpose of alignment spot separating feature:
- Sometimes compounds with the same mass with different structures (isomeric compounds) tend to overlap in mass spectrometry data, making it difficult for users to distinguish between them.
- By duplicating an alignment spot, users can separate and accurately analyze each isomeric compound individually, ensuring their unique retention times and peak intensity are properly captured.
Step-by-Step workflow for duplicating alignment spot features to separate isomers in the GUI
This tutorial demonstrates how to separate isomeric compounds in lipidomics and metabolomics projects by duplicating alignment spot features. The process is designed to be efficient, with minimal time requirements. Start by opening MS-DIAL 5.3. Next, select and open your processed lipidomics or metabolomics project to load it into the software. Once your project is loaded, you will see the alignment result window displaying your data (eg., lipidomics data) within MS-DIAL.
Next, click on “Show Ion Table” to view the lipids annotated by MS-DIAL. Further, proceed with the peak picking process. If you identify isomeric compounds within your data, follow the subsequent steps to separate those isomeric mixtures effectively (Figure 1).
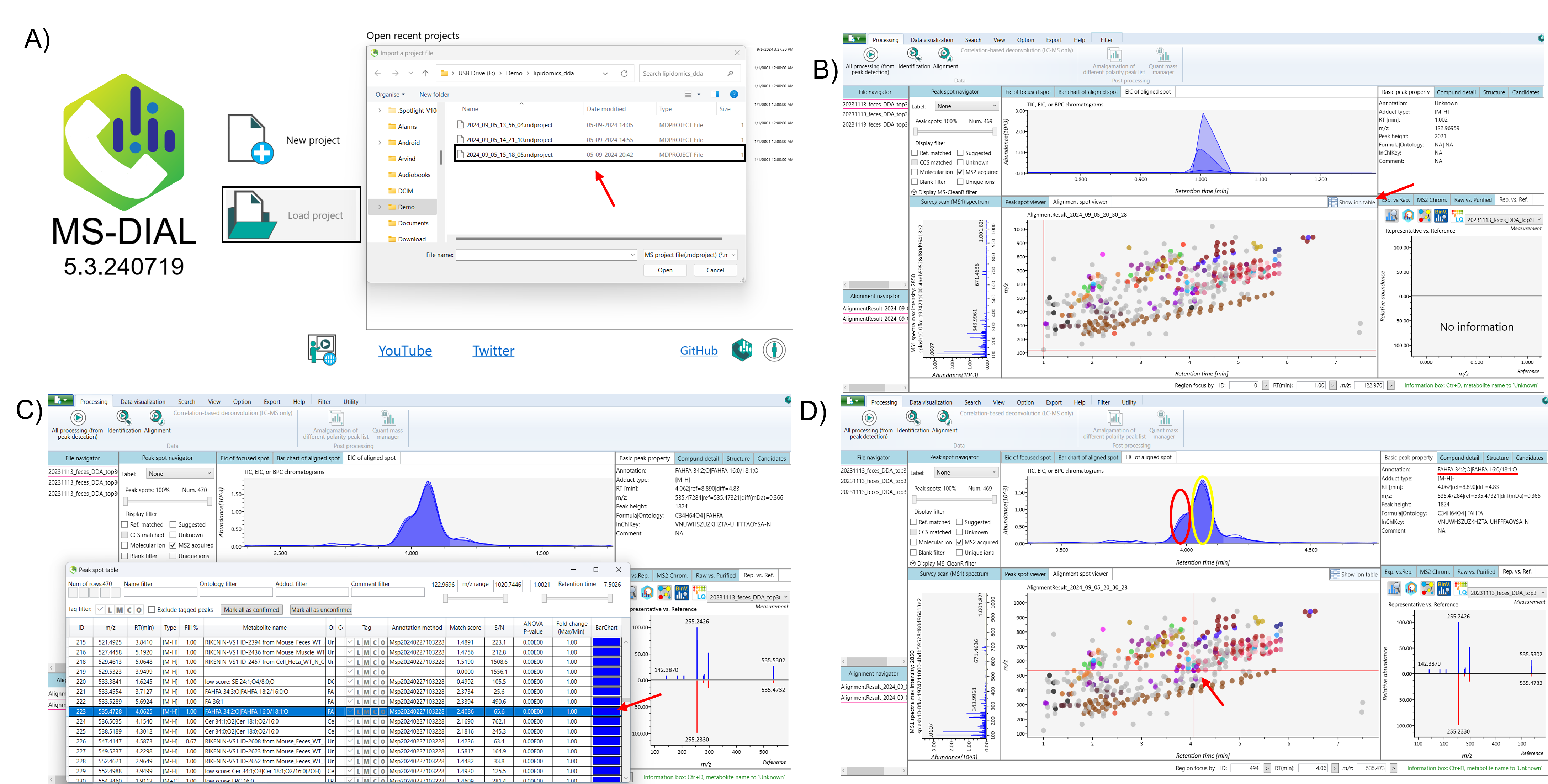
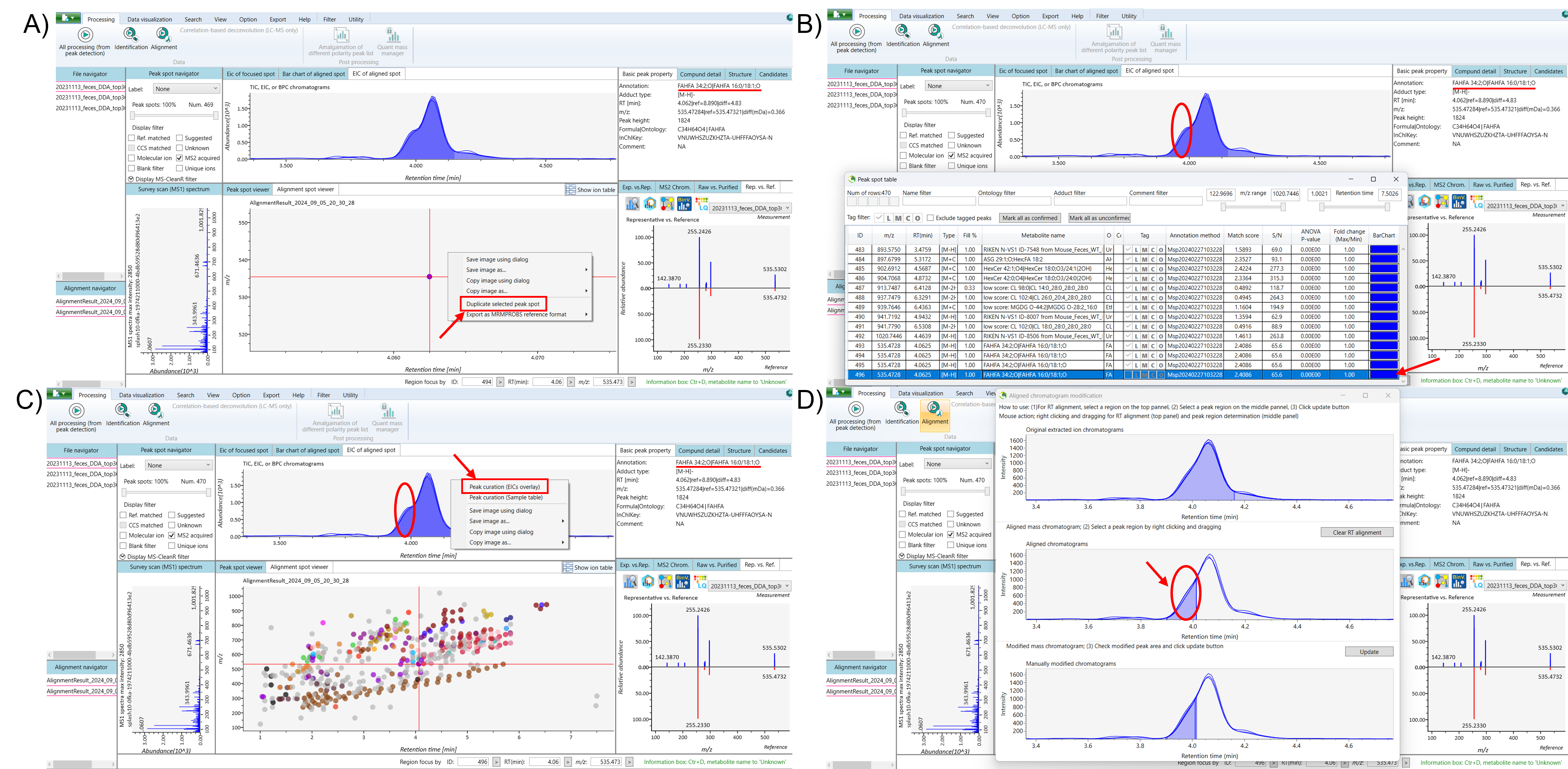
Select the lipid that appears as isomers in the ion table. Next, navigate to the EIC (Extracted Ion Chromatogram) of the aligned spot to view the peaks, and use the alignment spot viewer to examine the isomeric compounds. To duplicate the isomeric peaks, right-click and drag to zoom in on the alignment spot of the isomeric compounds within the alignment spot viewer. Then, right-click on the aligned spot and select “Duplicate Selected Peak Spot.” Finally, return to the ion table, where the duplicated peak of the isomeric compound, will appear at the bottom.
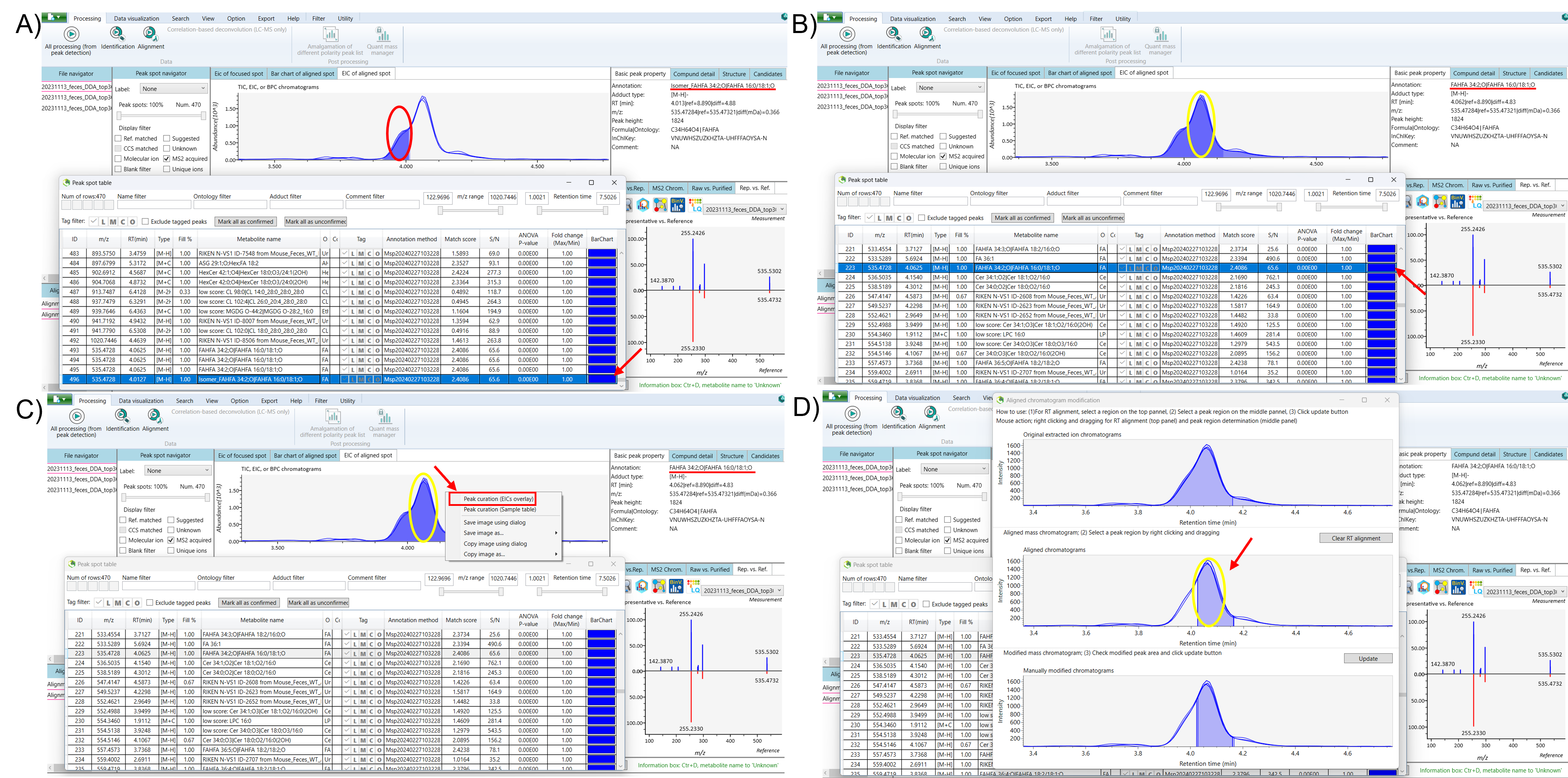
Select the duplicated isomeric peak and recheck the peaks in the EIC of the aligned spot. Minimize the ion table, then right-click on the EIC of the aligned spot and select “Peak Curation (EICs Overlay)” to begin separating the isomers. The “Aligned Chromatogram Modification” window will appear, displaying the original EIC, aligned chromatograms, and manually modified chromatograms. Right-click on the aligned chromatograms and drag to select the low-intensity peak of the duplicated isomer, and click “Update.” After updating, close the “Aligned Chromatogram Modification” window, reopen the ion table, and refresh the list. The separated isomeric peak of the duplicated isomer can now be seen in the EIC of the aligned spot. For better clarity, consider renaming the duplicate peak to facilitate understanding (Figure 2 and 3).
Next, open the ion table and select the original isomeric peak. Follow a similar process to separate this peak by rechecking the peaks in the EIC of the aligned spot. Right-click on the EIC of the aligned spot and choose the “Peak Curation (EICs Overlay)” option to begin the separation process. In the “Aligned Chromatogram Modification” window, right-click and drag to select the high-intensity peak of the original isomeric peak from the aligned chromatograms, then click “Update” to apply the changes. After updating, refresh the ion table to see the separated peak intensity of the original isomeric peak, distinct from the duplicated isomer (Figure 3).
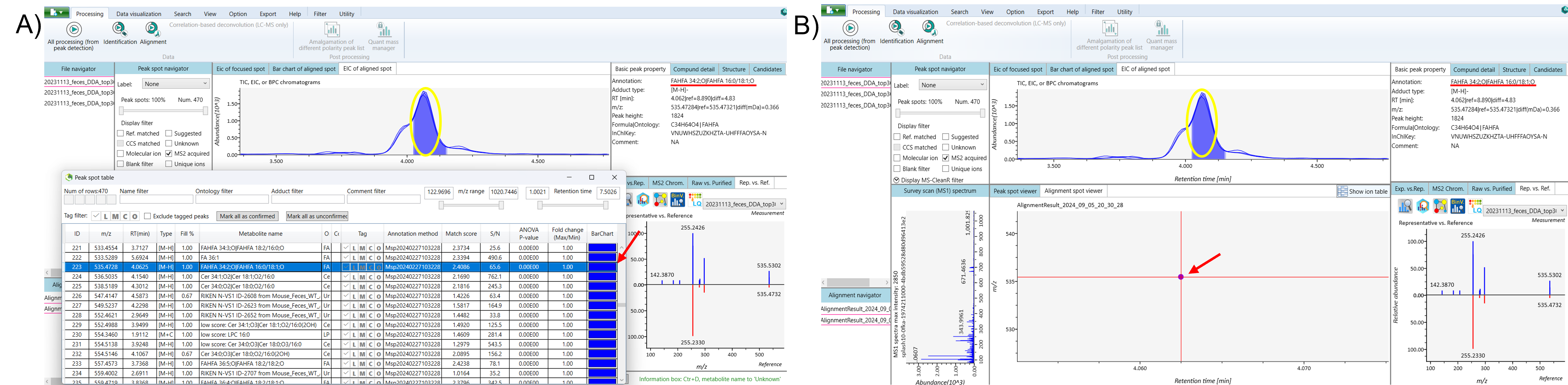
To get a clearer view, right-click and drag to zoom in on the alignment spot of the separated isomeric peak within the Alignment Spot Viewer. Finally, save your project and export the results (Figure 4).
The video for using this feature can be found below